What Is The Difference Between Mitosis In Plant And Animal Cells
Main Departure – Creature Mitosis vs Establish Mitosis
Beast and plant mitosis are two types of reproductive nuclear divisions in animals and plants, respectively. During mitosis, the amount of the genetic fabric remains as the same. Hence, it increases the number of cells in the body during growth, repair, and regeneration. Mitosis occurs in four major steps; prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The chief difference between animal mitosis and plant mitosis is that the mitotic spindle in animal mitosis is formed with the help of ii centrioles whereas mitotic spindle in constitute mitosis is formed without any centrioles. Mitosis is followed by cytokinesis.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is Creature Mitosis
– Definition, Process, Features
2. What is Institute Mitosis
– Definition, Process, Features
3. What are the Similarities Betwixt Animal and Constitute Mitosis
– Outline of Mutual Features
iv. What is the Divergence Between Animal and Found Mitosis
– Comparison of Key Differences
Key Terms: Anaphase, Creature Mitosis, Centrioles, Metaphase, Mitotic Spindle, Institute Mitosis, Prophase, Reproductive Cell Division, Telophase 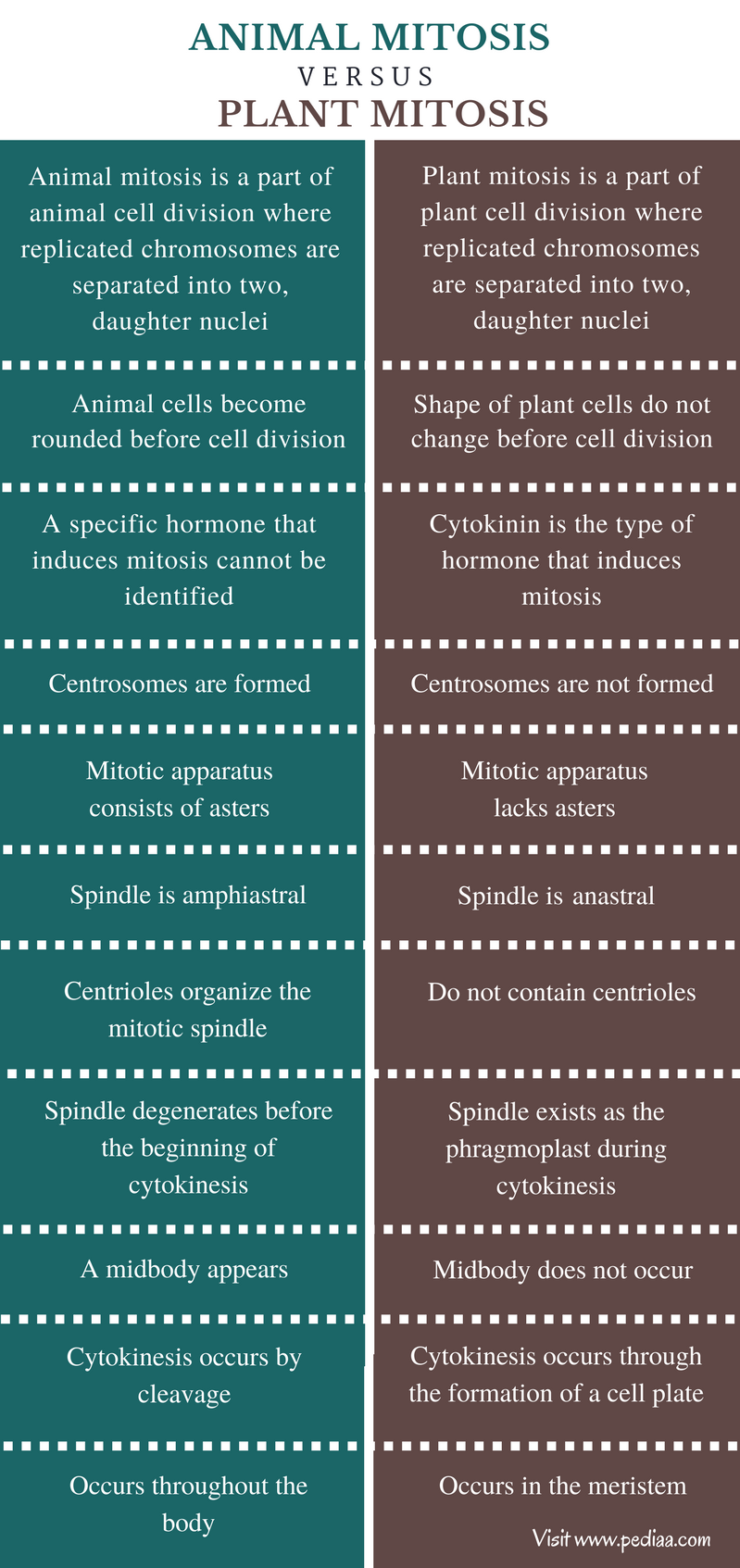
What is Animal Mitosis
Animate being mitosis refers to a part of the prison cell cycle of animal cells where replicated chromosomes are separated into ii, daughter nuclei. This ways nuclear division occurs during mitosis. Earlier entering into the mitotic division, the prison cell exists in the interphase. Animal mitosis occurs in four major steps: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus is condensed into chromosomes. Since DNA is replicated during interphase, each individual chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. The microtubules, which are involved in maintaining the shape of the cell, are disassembled to form the mitotic spindle. Therefore, the shape of the jail cell becomes circular. The organization of the microtubules into the mitotic spindle is done past centrioles, which occur in each pole. The breakup of the nuclear envelope occurs in prometaphase. Each sis chromatid joins with the spindle fibers. Private chromosomes are aligned in the cell equator during metaphase.
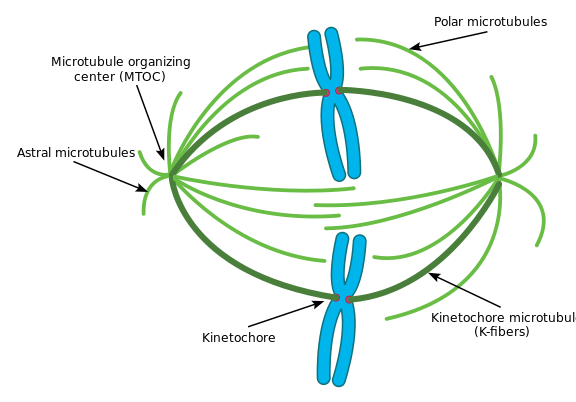
Figure ane: Animal Mitotic Spindle
During anaphase, each sister chromatid is separated from the centromere and begins to motility into the contrary poles of the jail cell. At this time, the individual sis chromatids are called daughter chromosomes. During telophase, ane ready of daughter chromosomes has arrived at the each contrary pole of the cell. Therefore, nuclear envelope is formed, surrounding the genetic fabric in the each pole. Mitosis is followed past cytoplasmic partitioning, which is called cytokinesis. Creature cell cytokinesis occurs by the formation of a cleavage furrow. The spindle appliance of the animal cell mitosis is shown in figure i.
What is Found Mitosis
Plant mitosis is a part of institute cell division where the replicated chromosomes are separated into two, daughter nuclei. It occurs in four stages, aforementioned equally animal mitosis. These stages are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromatin is condensed into individual chromosomes. The formation of the mitotic spindle in plants is unlike from animal mitotic spindle germination. Plants do not possess microtubules organization centers such as centrioles or spindle pole bodies. Therefore, microtubules are nucleated nearly the nuclear envelope, forming the mitotic spindle. Metaphase, anaphase, and telophase occur as same every bit in animal mitosis.
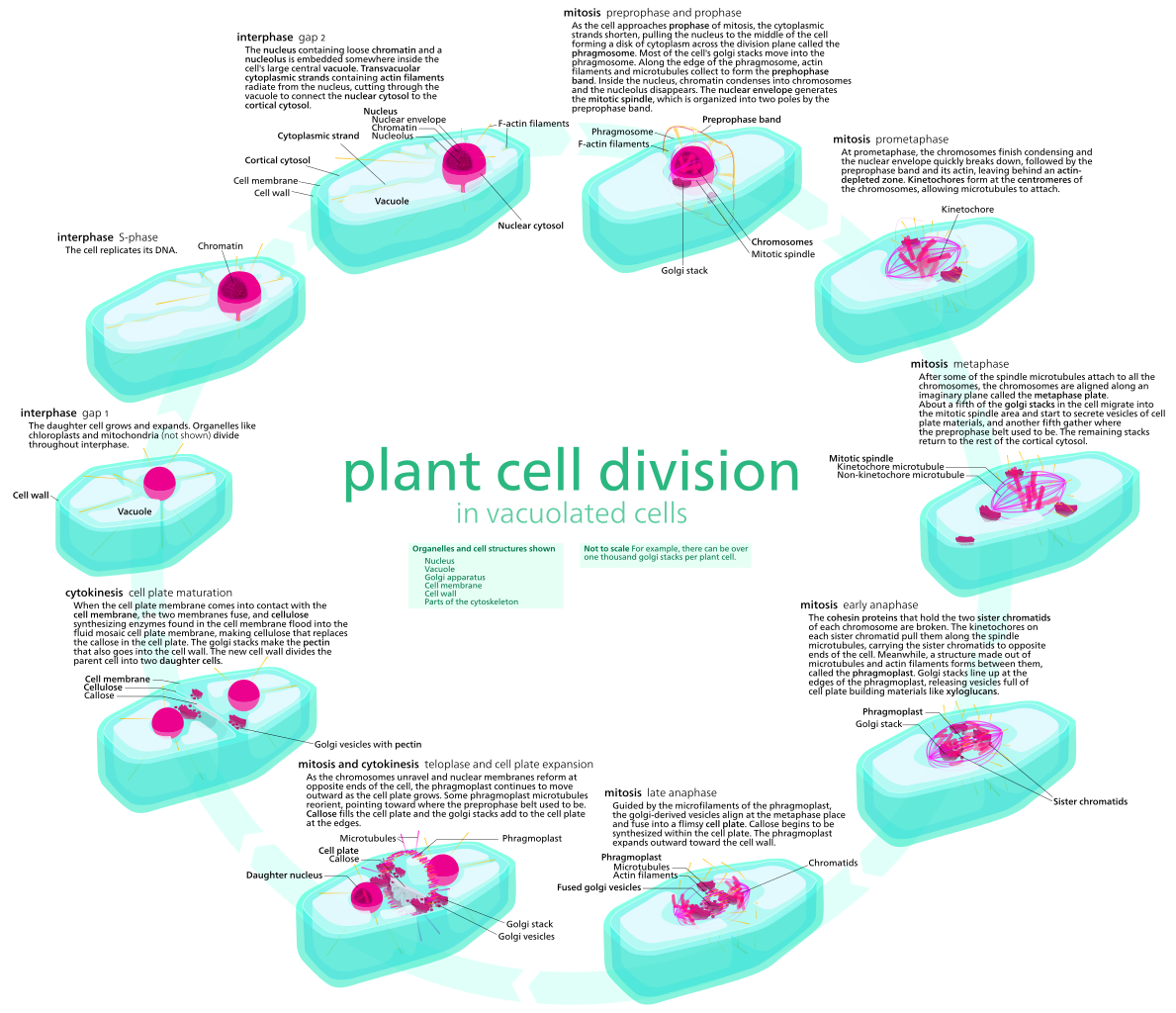
Figure 2: Plant Jail cell Division
Plant mitosis is followed by cytokinesis. Cytoplasmic division occurs by the formation of a cell plate, separating the two girl nuclei, which is formed at the end of the telophase. The microtubules of the mitotic spindle are bundled into the phragmoplast, which serves equally a scaffold to the formation of the cell plate. The cell plate develops into a new prison cell wall. The plant prison cell division is shown in figure ii.
Similarities Between Animate being and Plant Mitosis
- Both animal and found mitosis occur to increase the number of cells in the body, to repair body tissues, and to regenerate torso parts.
- Both processes occur in four major steps: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Both animal mitosis and plant mitosis are followed past cytoplasmic division.
- During prophase, the chromosome condensation occurs in both animal and establish mitosis.
- The breakup of the nuclear envelope occurs in the prometaphase. Individual chromosomes also move the metaphase plate. The spindle attaches to the chromosomes as well.
- Private chromosomes are arranged on the metaphase plate during metaphase.
- Sis chromatids motility towards the reverse poles during anaphase.
- In telophase, the reappearance of the nuclear envelope tin can be identified.
Deviation Between Beast and Institute Mitosis
Definition
Animal Mitosis: Animal mitosis is a function of animal jail cell division where replicated chromosomes are separated into two, daughter nuclei.
Plant Mitosis: Plant mitosis is a office of plant jail cell division where replicated chromosomes are separated into two, girl nuclei.
Shape
Animal Mitosis: The animal cells become rounded earlier cell division.
Plant Mitosis: The shape of plant cells practise not change earlier cell sectionalization.
Induction of the Mitosis
Animal Mitosis: A specific hormone that induces mitosis cannot exist identified.
Plant Mitosis: Cytokinin is the type of hormone that induces mitosis.
Centrosome
Animal Mitosis: Centrosomes are formed during animal mitosis.
Plant Mitosis: Centrosomes are not formed during establish mitosis.
Asters in the Mitotic Apparatus
Animal Mitosis: The mitotic apparatus consists of asters.
Plant Mitosis: The mitotic apparatus lacks asters.
Spindle
Beast Mitosis: The spindle that occurs in the animal mitosis is amphiastral.
Constitute Mitosis: The spindle that occurs in the plant mitosis is anastral.
Centrioles
Animal Mitosis: Centrioles organize the mitotic spindle during the animal mitosis.
Plant Mitosis: Found cells lack centrioles.
Spindle at the Cytokinesis
Animal Mitosis: The spindle degenerates before the showtime of cytokinesis.
Institute Mitosis: The spindle exists equally the phragmoplast during cytokinesis.
Midbody
Animal Mitosis: A midbody appears during the animal mitosis.
Plant Mitosis: Midbody does non occur in the plant mitosis.
Cytokinesis
Beast Mitosis: Cytokinesis occurs by cleavage in animal mitosis.
Plant Mitosis: Cytokinesis occurs through the formation of a prison cell plate in constitute mitosis.
Occur in
Beast Mitosis: Animal mitosis occurs throughout the body.
Plant Mitosis: Institute mitosis occurs in the meristem.
Decision
Creature and plant mitosis are ii types of reproductive jail cell divisions, which are used to increase the cell number in animals and plants, respectively. Both creature mitosis and institute mitosis produce two girl cells with the same amount of genetic textile. Both processes occur through four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Though all stages are same in both animal and plant mitosis, the formation of the mitotic spindle is different. Animal cells comprise centrioles, which nucleate the microtubules of the spindle. Since plant cells lack centrioles, the microtubules are nucleated virtually the nuclear envelope. Therefore, the chief difference between animal and establish mitosis is the formation of the mitotic spindle.
Reference:
1."Brute Cell Mitosis ." CELLS alive!, Available hither. Accessed 29 Sept. 2017.
two."Phases of mitosis." Khan Academy, Available here. Accessed 29 Sept. 2017.
Prototype Courtesy:
ane. "Spindle apparatus" By Lordjuppiter – Own piece of work (CC By-SA iii.0) via Commons Wikimedia
two. "Plant prison cell cycle" Past Kelvinsong – Own work (CC Past-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia

Source: https://pediaa.com/difference-between-animal-and-plant-mitosis/
Posted by: davisdorbacted.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Difference Between Mitosis In Plant And Animal Cells"
Post a Comment